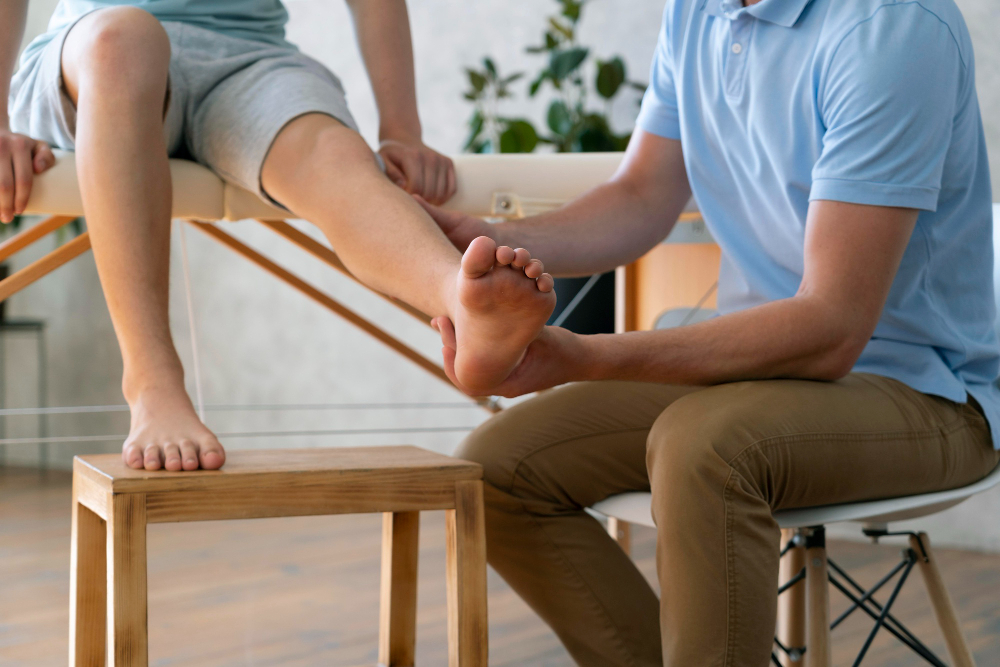
Shin splints, a common ailment among athletes, can also affect older adults. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes of shin splints in older individuals and explore effective management strategies. Whether you’re an active senior or a concerned caregiver, understanding and addressing shin splint pain is crucial for maintaining mobility and overall well-being.
Causes of Shin Splints in Older Adults
As we age, our bones and muscles undergo natural changes, which can, in turn, contribute to the development of shin splints. Factors such as reduced bone density, weakened muscles, and altered biomechanics play a pivotal role in this process. Therefore, it becomes essential to recognize these underlying causes in order to implement targeted strategies for prevention and effective relief.
- Reduced Bone Density
Ageing often brings about a decline in bone density, a key factor contributing to shin splint pain. As bones become more porous and fragile, the lower leg may experience heightened stress during weight-bearing activities, exacerbating discomfort. This decline in bone density underscores the importance of incorporating strategies to enhance bone health, such as proper nutrition and targeted exercises. - Weakened Muscles
The natural ageing process leads to muscle loss and decreased strength, particularly in the lower extremities. Weakened muscles in the shin area may struggle to provide adequate support during physical activities, contributing to shin splint pain. Strengthening exercises tailored to the calf muscles become crucial, acting as a protective measure against the strain that can lead to shin splints. - Altered Biomechanics
Changes in biomechanics, including alterations in gait and foot mechanics, play a significant role in shin splints among older adults. These biomechanical shifts can create uneven stress distribution along the shin, resulting in pain and discomfort. Addressing altered biomechanics involves gait analysis and corrective measures, such as orthotic devices or supportive footwear, to restore optimal lower limb alignment. - Impacts of Previous Injuries
Older adults may carry the legacy of previous injuries, such as fractures or sprains, which can predispose them to shin splints. Scar tissue and residual weakness from past injuries may contribute to an increased vulnerability to shin splint pain. Rehabilitation exercises and ongoing monitoring become essential to mitigate the long-term effects of prior injuries. - Overuse and Insufficient Recovery
Engaging in repetitive high-impact activities without adequate recovery time can lead to overuse injuries, including shin splints. Older adults may unknowingly subject their shins to excessive stress, especially if they lead active lifestyles. Balancing physical activity with sufficient rest intervals becomes crucial in preventing overuse-related shin splint pain.
Tailored Exercises for Shin Splint Relief
For those already experiencing shin splints, tailored exercises can provide relief and aid in the recovery process. Let’s explore specific exercises designed to alleviate pain and strengthen the affected areas.
- Toe Taps
While seated, gently tap your toes on the floor for 1-2 minutes. This low-impact exercise helps improve circulation and flexibility in the calf muscles. - Calf Raises
Stand with your feet separated at hip-width, then gradually elevate your heels from the ground, lifting yourself onto your toes. Hold for a few seconds before lowering. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions. - Towel Stretch
Sit on the floor with your legs extended. Loop a towel around the ball of your foot and gently pull it towards you, feeling a stretch in your calf. Maintain the position for 15 to 30 seconds on each leg. - Ankle Alphabet
While seated, lift one foot off the ground and draw the alphabet with your toes. This exercise promotes ankle mobility and engages the calf muscles. - Seated Shin Stretch
Sit on your heels with your knees bent and toes pointed. Gently lean back to feel a stretch in the shins. Hold for about 15 to 30 seconds, repeating as necessary. - Heel Drops
Stand on a step with your heels extending beyond the edge. Lower your heels below the step and then lift them back up. Perform 10-15 repetitions to strengthen the calf muscles.
Similar Ailments to Shin Splints: Understanding the Differences and Remedies
While shin splints are a common lower leg concern, there are several other conditions that share similarities in symptoms or causes. It’s crucial to distinguish between these ailments for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. So let’s delve into some of the similar conditions and explore their unique characteristics.
- Stress Fractures
Symptoms:
Stress fractures involve tiny cracks in the bones, leading to localised pain and tenderness. The discomfort typically increases with weight-bearing activities.
Distinguishing Factor:
Stress fractures are specific to bone injuries, often caused by repetitive impact or overuse. X-rays or bone scans may be necessary for diagnosis.
Remedies:
Rest, reduced weight-bearing activities, and sometimes immobilisation with a brace or cast are common approaches. Adequate nutrition for bone health is crucial for recovery. - Compartment Syndrome
Symptoms:
Compartment syndrome results from increased pressure within the muscles, causing pain, swelling, and potential numbness or weakness.
Distinguishing Factor:
Unlike shin splints, compartment syndrome involves pressure within muscle compartments. It may require pressure measurement tests for diagnosis.
Remedies:
Adjustments in activity levels, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery to release pressure within the affected compartment. - Tendonitis
Symptoms:
Tendonitis is inflammation of the tendons, leading to pain, swelling, and sometimes warmth around the affected area.
Distinguishing Factor:
Tendonitis focuses on the inflammation of tendons, often caused by repetitive motions. The diagnosis for this includes imaging studies and a physical examination.
Remedies:
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.), along with anti-inflammatory medications and targeted exercises for tendon health. - Muscle Strains
Symptoms:
Muscle strains involve the stretching or tearing of muscle fibres, resulting in pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
Distinguishing Factor:
Strains are specific to muscle injuries, often caused by sudden or excessive force. Diagnosis relies on clinical assessment and imaging studies.
Remedies:
Rest, ice, and gentle stretching exercises are common approaches for managing muscle strains. For severe cases, the recommendation might include physical therapy. - Periostitis
Symptoms:
Periostitis is inflammation of the periosteum, the connective tissue covering bones, causing localised pain and tenderness.
Distinguishing Factor:
It involves inflammation of the bone’s outer layer, often due to repetitive stress. Diagnosis may involve imaging studies and clinical evaluation.
Remedies:
Rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and modifying activities to reduce stress on the affected area.
Bucksfoot Clinic: Your Trusted Partner in Toe Care
Shin splints in older adults are a manageable condition with the right knowledge and proactive measures. Whether you’re an older individual experiencing shin splint pain or a caregiver seeking ways to support a loved one, these strategies aim to enhance overall leg health and maintain an active lifestyle. So if you wish to seek the best tailored treatments for your foot health, contact Bucksfoot. Visit our website to learn more.
FAQs
Is it advisable for older adults with shin splints to continue exercising?
Yes, low-impact exercises that don’t exacerbate shin splint pain can contribute to overall fitness and well-being.
Are there lifestyle adjustments that can alleviate shin splint pain?
Lifestyle adjustments such as proper footwear and biomechanical considerations can significantly alleviate shin splint pain.
Can older adults with shin splints benefit from orthopaedic interventions?
Orthopaedic interventions, including orthotic inserts, can provide additional support and reduce shin splint discomfort.
How soon should one seek medical advice for shin splints in older adults?
If shin splint pain persists or worsens, seeking medical advice promptly is recommended to identify the underlying cause and implement appropriate management strategies.
How does reduced bone density contribute to shin splints?
Reduced bone density makes bones more susceptible to stress fractures and inflammation, increasing the risk of shin splints
Can physical therapy help manage shin splints in older adults?
Yes, physical therapy techniques, including massage and targeted exercises, can effectively manage shin splint pain.
Can shin splints in older adults be prevented?
Yes, preventive measures include proper footwear, low-impact exercises, and regular stretching
Are there specific exercises older adults can do to strengthen calf muscles?
Absolutely, targeted calf-strengthening exercises are beneficial; consult a healthcare professional for personalised recommendations.